Microgreens: Summary of Nutritional Properties and Health Benefits

Health Benefits
Microgreens are a concentrated source of nutrients and bioactive compounds that can provide a wide range of health benefits. Here are the benefits of some of the most important nutrients found in microgreens:
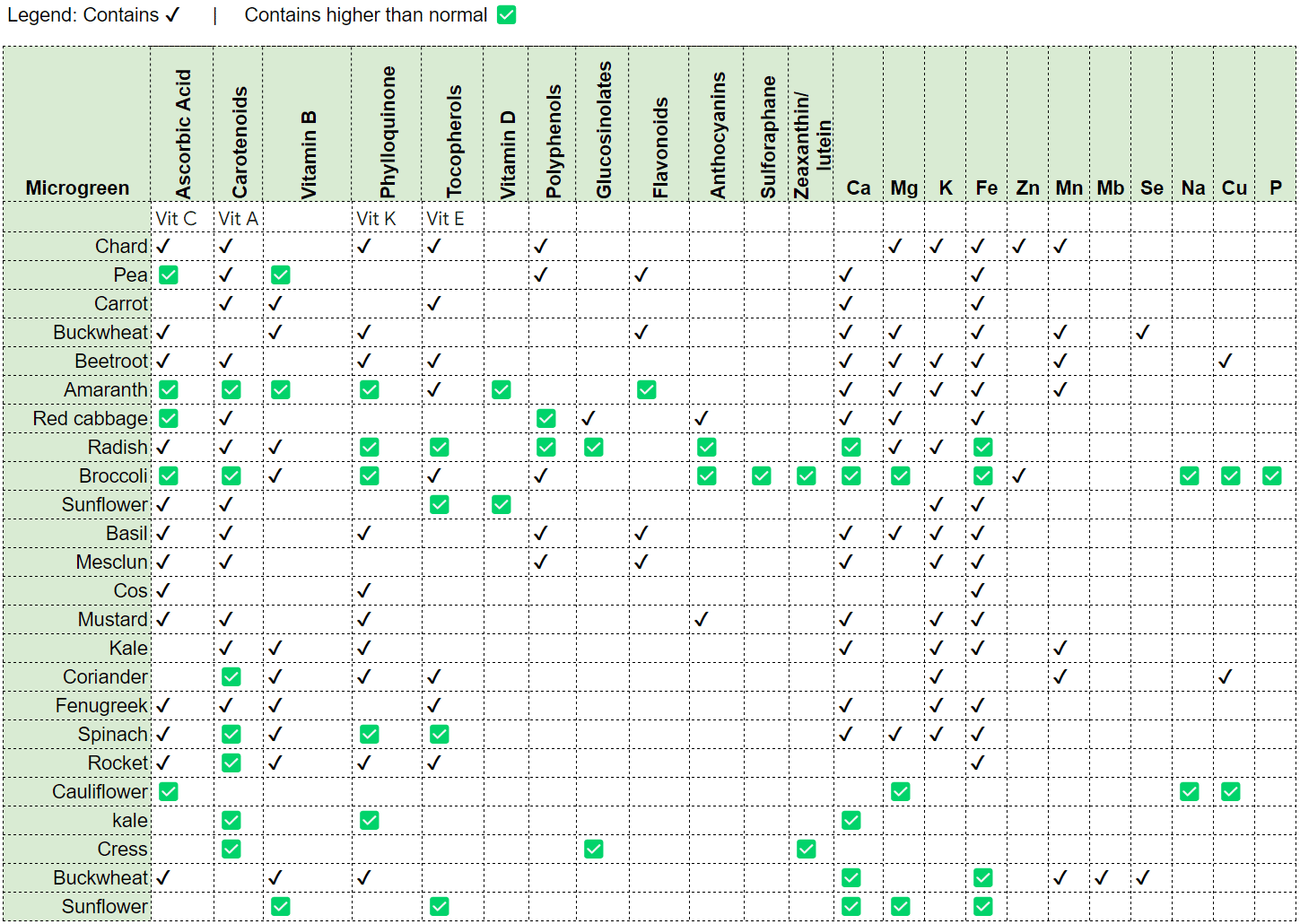
Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C): Ascorbic acid is essential for the immune system, as it stimulates the production of white blood cells and acts as an antioxidant, fighting oxidative stress and protecting cells against damage. It is also necessary for collagen formation, which keeps skin, joints and blood vessels healthy.
Carotenoids: Carotenoids, such as beta-carotene, are precursors to vitamin A. They play a vital role in eye health, strengthening vision and reducing the risk of eye diseases, such as macular degeneration.
Vitamin K: Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting, which prevents excessive bleeding. It is also crucial for bone health, as it helps fix calcium in the bones and prevents calcification of the arteries.
Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that protects cells from free radical damage. It can also help maintain healthy skin and prevent premature aging.
B Vitamins: B vitamins, such as B1 (thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B6 (pyridoxine), B9 (folic acid) and B12 (cobalamin), play a crucial role in energy production, nervous system function and DNA synthesis. They are also essential for heart health and brain function.
Polyphenols: Polyphenols are bioactive compounds that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They can protect against chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease and promote brain health.
Glucosinolates: Glucosinolates are compounds present in cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli and radish) and have been associated with cancer prevention. They can stimulate the body's detoxification and reduce inflammation.
Flavonoids: Flavonoids are antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables and herbs. They contribute to cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and improving blood vessel function.
Anthocyanins: Anthocyanins are compounds that give foods their purple or blue color, such as berries and purple cabbage. They have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may protect against chronic diseases and improve memory and brain health.
Minerals (Magnesium, Potassium, Zinc, Selenium, Iron, Calcium): These minerals are critical for a variety of bodily functions. Magnesium and potassium are essential for cardiovascular health and muscle function. Zinc and selenium are vital for the immune system and skin health. Iron is necessary to prevent anemia, and calcium is essential for bone health and blood clotting.
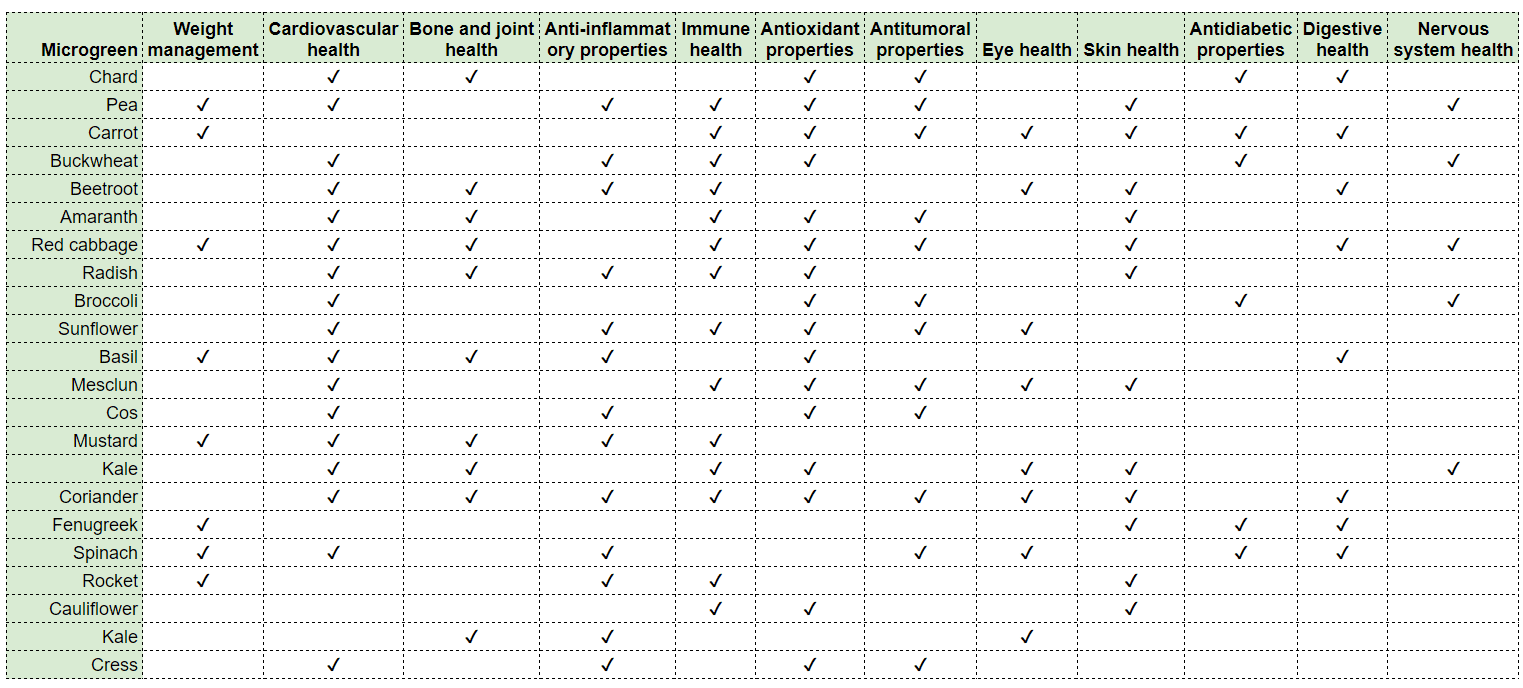
In summary, microgreens are a rich and concentrated source of essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that can have a significant impact on health. By incorporating a variety of microgreens into your diet, you can take advantage of a wide range of health benefits, ranging from protection against chronic diseases to strengthening the immune system and improving overall health.
Nutritional Properties
Health Benefits Summary
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The author and publisher of this article are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of any suggestions, preparations, or procedures described in this article.
References
Lester, Gene & Xiao, Zhenlei & Luo, Yaguang & Wang, Qin. (2013). Microgreens: Assessment of Nutrient Concentrations. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267354000_Microgreens_Assessment_of_Nutrient_Concentrations
Bhaswant, M., Shanmugam, D. K., Miyazawa, T., Abe, C., & Miyazawa, T. (2023). Microgreens—A comprehensive review of bioactive molecules and health benefits. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 28(2), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020867
Choe, U., Yu, L. L., & Wang, T. T. Y. (2018). The science behind microgreens as an exciting new food for the 21st century. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(44), 11519–11530. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03096
Reddy, M., Vadlamudi, K., & Ganesh, B. (n.d.). Role of microgreens and their potential health benefits: A review. Jetir.org. Retrieved October 27, 2023, from https://www.jetir.org/papers/JETIR2105366.pdf
Renna, M., & Paradiso, V. M. (2020). Ongoing research on microgreens: Nutritional properties, shelf-life, sustainable production, innovative growing and processing approaches. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 9(6), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060826
Xiao, Z., Lester, G. E., Luo, Y., & Wang, Q. (2012). Assessment of vitamin and carotenoid concentrations of emerging food products: Edible microgreens. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(31), 7644–7651. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf300459b
Xiao, Z., Rausch, S. R., Luo, Y., Sun, J., Yu, L., Wang, Q., Chen, P., Yu, L., & Stommel, J. R. (2019). Microgreens of Brassicaceae: Genetic diversity of phytochemical concentrations and antioxidant capacity. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft Und Technologie [Food Science and Technology], 101, 731–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.076
Zhang, Y., Xiao, Z., Ager, E., Kong, L., & Tan, L. (2021). Nutritional quality and health benefits of microgreens, a crop of modern agriculture. Journal of Future Foods, 1(1), 58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfutfo.2021.07.001

