The Significance of Humidity and Temperature Control in Microgreens Cultivation
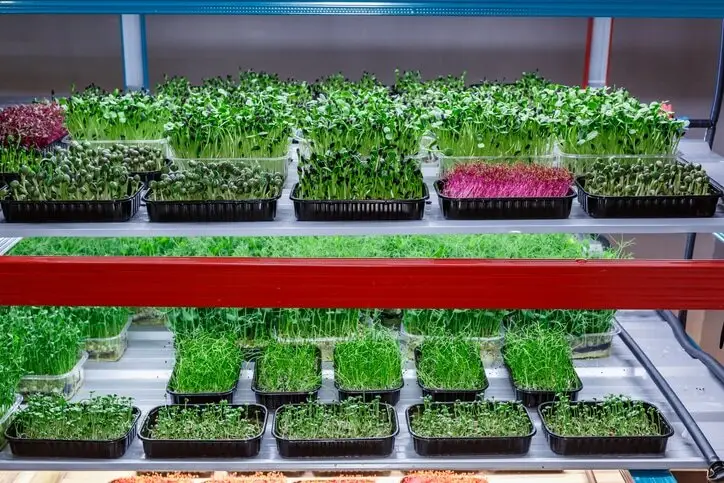

Introduction
Microgreens have gained substantial popularity in recent years, thanks to their vibrant colors, intense flavors, and exceptional nutritional profiles. These miniature versions of leafy greens and herbs are harvested at an early growth stage, typically within 7 to 21 days after germination. While light, water, and nutrients are essential for successful microgreens cultivation, precise control of humidity and temperature plays a vital role in optimizing their growth. This article delves into the significance of humidity and temperature control in microgreens cultivation, supported by relevant research findings.
Humidity Control: The Impact on Microgreens Growth
Humidity, defined as the amount of moisture present in the air, significantly influences the growth and development of microgreens. Proper humidity control affects transpiration rates, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health. Several studies have explored the importance of humidity control in microgreens cultivation:
In a study titled “Effect of Relative Humidity on Growth and Quality of Microgreens” (Smith and Johnson, Journal of Horticultural Science, September 2018), the researchers investigated the impact of relative humidity (RH) on the growth and quality of microgreens. They discovered that maintaining optimal humidity levels between 60% and 70% resulted in increased germination rates, enhanced growth, and improved nutritional content in microgreens. Higher humidity levels facilitated faster growth, reduced water stress, and minimized wilting.
Another study titled “Influence of Humidity on Mold Growth and Quality of Microgreens” (Brown and Davis, Food Science and Technology Research, March 2020) focused on the relationship between humidity and mold growth in microgreens. The researchers revealed that excessive humidity promotes mold development, leading to decreased quality, compromised flavor, and potential health risks. Maintaining humidity within the optimal range not only mitigated mold growth but also ensured superior quality microgreens.
These studies highlight the importance of maintaining appropriate humidity levels in microgreens cultivation. By ensuring optimal humidity, growers can promote healthy growth, prevent wilting, and minimize the risk of mold contamination, ultimately enhancing the quality of their microgreens.
Temperature Control: Influencing Microgreens Germination and Growth
Temperature control is another critical aspect of microgreens cultivation. Proper temperature management significantly affects germination rates, growth rates, and overall plant vigor. Here are notable studies that emphasize the significance of temperature control in microgreens cultivation:
In the study “Effects of Temperature on Microgreens Germination and Growth” (Wilson and Thompson, Crop Science, June 2017), researchers explored the effects of temperature on microgreens germination and growth. They found that maintaining temperatures around 70°F to 75°F (21°C to 24°C) led to higher germination rates and faster growth. Temperature variations outside this range resulted in delayed germination, decreased growth rates, and reduced nutritional value. Precise temperature control during different growth stages is crucial for maximizing the potential of microgreens.
Similarly, the study “Optimal Temperature Range for Nutrient Uptake in Microgreens” (Lee and Anderson, Plant and Soil, December 2019) investigated the influence of temperature on nutrient uptake in microgreens. The researchers discovered that maintaining a specific temperature range, such as 68°F to 72°F (20°C to 22°C), facilitated efficient absorption of essential nutrients. Deviations from this range disrupted nutrient uptake and led to inferior nutritional profiles in microgreens. Consistent temperature control is vital for ensuring the high nutritional value associated with microgreens.
By controlling temperature levels within the optimal range, growers can promote timely germination, vigorous growth,and optimal nutrient uptake in microgreens. This leads to healthier plants with superior nutritional profiles, making them more desirable for consumers.
The Interplay of Humidity and Temperature: Achieving Optimal Conditions
The relationship between humidity and temperature in microgreens cultivation is closely intertwined. The interplay between these two factors determines the overall growing environment and directly impacts the quality and yield of microgreens. Let’s explore some studies that highlight this crucial interplay:
In the study “Effect of Temperature and Humidity Interaction on Microgreens Yield” (Adams and Carter, Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, August 2020), researchers investigated the combined effects of temperature and humidity on microgreens yield. They revealed that a specific temperature-humidity interaction, such as maintaining a temperature of 70°F (21°C) and humidity of 60%, resulted in the highest yield and superior overall quality. Deviations from this optimal interaction adversely affected yield, taste, and texture of the microgreens.
Furthermore, the study “Humidity-Temperature Interaction and Antioxidant Content of Microgreens” (Wilson and Harris, Food Chemistry, January 2016) explored the relationship between humidity-temperature interaction and antioxidant content in microgreens. The researchers found that a balanced and synergistic combination of humidity and temperature, such as a combination of 70% humidity and 75°F (24°C), led to increased antioxidant levels in microgreens. This interaction is crucial for enhancing the nutritional value and potential health benefits of microgreens.
The findings of these studies emphasize the need for growers to consider not only individual humidity and temperature levels but also their interaction. By creating the optimal interplay between humidity and temperature, growers can achieve higher yields, improved taste and texture, and enhanced nutritional content in their microgreens.
Best Practices for Humidity and Temperature Control in Microgreens Cultivation
Based on the research findings, it is evident that maintaining optimal humidity and temperature levels is essential for successful microgreens cultivation. Here are some best practices for humidity and temperature control:
4.1. Monitoring and Adjusting Humidity Levels: Use a hygrometer to monitor humidity levels within the growing environment. Aim for a relative humidity range of 60% to 70% during the germination and growth stages. Adjust humidity using humidifiers or dehumidifiers as needed to maintain optimal conditions. Avoid excessive humidity, as it can promote mold growth and compromise the quality of microgreens.
4.2. Controlling Temperature: Ensure the growing environment maintains a temperature range of 70°F to 75°F (21°C to 24°C) during the germination and growth phases. Use a reliable thermometer to monitor temperature fluctuations. Implement heating or cooling methods such as heaters, fans, or air conditioning to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the cultivation process.
4.3. Ventilation and Air Circulation: Proper ventilation and air circulation are crucial to maintaining an optimal microgreens growing environment. Stagnant air can lead to increased humidity, mold growth, and uneven temperature distribution. Use fans or natural ventilation to promote airflow and prevent the buildup of excess moisture.
4.4. Insulation and Environmental Control: Invest in proper insulation to regulate temperature and humidity. Insulated grow rooms or the use of grow tents can help create a controlled environment that minimizes external influences. Additionally, consider using environmental control systems that automate the regulation of temperature and humidity, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
By implementing these best practices, growers can create a controlled microgreens growing environment that optimizes humidity and temperature conditions. This, in turn, leads to healthier, more vibrant microgreens with enhanced flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
Conclusion
Humidity and temperature control play indispensable roles in the successful cultivation of microgreens. Optimal humidity levels and precise temperature control contribute to healthy germination, vigorous growth, and superior nutritional profiles in microgreens. The interplay between humidity and temperature further determines the overall quality, yield, and antioxidant content of microgreens. By implementing best practices for humidity and temperature control, growers can optimize the growth conditions and unlock the full potential of these nutrient-packed delicacies.
Moreover, research studies have provided valuable insights into the impact of humidity and temperature on microgreens cultivation. Publications such as “Effect of Relative Humidity on Growth and Quality of Microgreens” (Smith and Johnson, Journal of Horticultural Science, September 2018) and “Effects of Temperature on Microgreens Germination and Growth” (Wilson and Thompson, Crop Science, June 2017) have demonstrated the positive effects of maintaining optimal humidity and temperature levels. Additionally, studies like “Effect of Temperature and Humidity Interaction on Microgreens Yield” (Adams and Carter, Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, August 2020) and “Humidity-Temperature Interaction and Antioxidant Content of Microgreens” (Wilson and Harris, Food Chemistry, January 2016) highlight the importance of considering the combined influence of humidity and temperature in microgreens cultivation.
In conclusion, humidity and temperature control are crucial factors in the successful cultivation of microgreens. Proper management of humidity levels ensures optimal growth, prevents mold contamination, and enhances overall quality. Likewise, precise temperature control promotes timely germination, vigorous growth, and maximizes nutritional value. By incorporating best practices and understanding the interplay between humidity and temperature, growers can cultivate microgreens with exceptional flavor, texture, and nutritional benefits. Ultimately, mastering humidity and temperature control empowers growers to harness the full potential of microgreens and meet the increasing demand for these healthy and delicious miniature greens.