Elevate Your Greenery: How to Incorporate Microgreens into a Vertical Garden or Green Wall
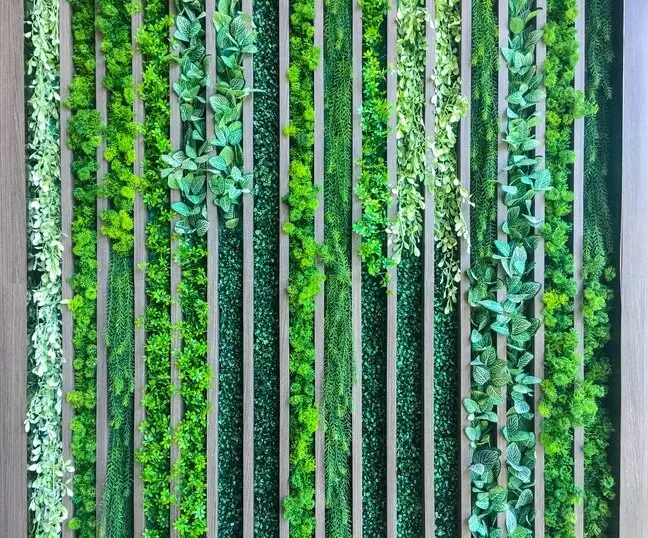

Introduction
Vertical gardens, also known as living walls or green walls, have become increasingly popular as innovative solutions for urban gardening and maximizing limited space. These vertical structures provide opportunities to bring nature indoors and create stunning visual displays. Integrating microgreens into a vertical garden or green wall takes the concept of vertical gardening to new heights, allowing you to enjoy fresh, nutrient-dense greens right at eye level. In this article, we will explore the steps and considerations involved in incorporating microgreens into a vertical garden, from selecting the right varieties to ensuring proper care and maintenance.
I. Understanding Microgreens and Vertical Gardens
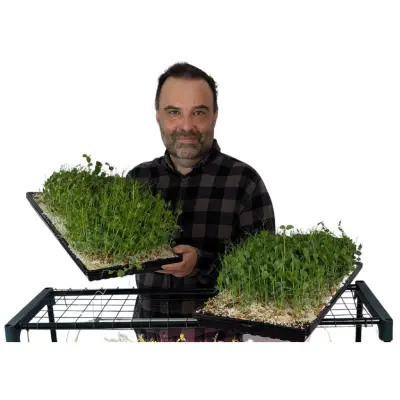
- Microgreens: Microgreens are young, tender seedlings of various vegetables and herbs. They are harvested at an early stage, usually when the first true leaves have developed. Microgreens offer concentrated flavors, vibrant colors, and a high nutritional value.
- Vertical Gardens: Vertical gardens or green walls are vertical structures designed to grow plants vertically, usually on a wall or freestanding framework. They are created using a variety of techniques, including modular systems, hydroponics, or soil-based systems. Vertical gardens allow for lush displays of greenery in both indoor and outdoor settings.
II. Selecting Microgreen Varieties for Vertical Gardens
- Consider Space and Lighting: Choose microgreen varieties that are well-suited to the available space and lighting conditions of your vertical garden. Some varieties thrive in low-light environments, while others require more sunlight. Examples of microgreens that adapt well to vertical gardens include kale, arugula, radish, and lettuce.
- Vibrant Colors and Leaf Shapes: Opt for microgreen varieties that offer a diverse range of colors and leaf shapes. This will enhance the visual appeal and create an artistic display on your vertical garden. Consider incorporating microgreens with contrasting colors, such as red-veined sorrel, purple basil, or rainbow chard.
III. Setting Up the Vertical Garden
- Choose the Right System: Select a vertical garden system that suits your space, budget, and desired aesthetics. Options include modular pocket systems, DIY pallet gardens, or custom-built frameworks. Ensure that the chosen system can support the weight of the plants and provide adequate support for the microgreens.
- Growing Medium: Determine the appropriate growing medium for your microgreens based on the chosen vertical garden system. Options include soil-based mixtures, soilless mediums (such as coco coir or peat moss), or hydroponic systems. Ensure the medium provides adequate moisture retention and drainage.
- Planting and Seeding: Follow the guidelines specific to the chosen microgreen varieties for seeding and planting. Consider the desired density and spacing of the microgreens on the vertical garden to create an attractive and balanced display.
IV. Care and Maintenance
- Watering: Proper watering is crucial for the success of microgreens in a vertical garden. Ensure that the growing medium remains consistently moist but not waterlogged. Consider using drip irrigation or a misting system to deliver water evenly throughout the vertical garden.
- Light Requirements: Assess the lighting conditions in the location of your vertical garden. Place it in an area that receives adequate natural light or supplement with artificial grow lights, especially for low-light environments. Position the microgreens according to their specific light requirements, placing light-loving varieties higher up in the vertical garden.
- Nutrient Supply: Depending on the chosen growing medium, microgreens may require additional nutrients to support healthy growth. Consider incorporating a balanced liquid fertilizer or organic amendments according to the specific needs of the microgreen varieties.
V. Harvesting and Enjoying Microgreens
- Harvesting Time: Microgreens are typically ready for harvest when the first true leaves have developed, which usually occurs within 1-3 weeks after seeding. Use clean scissors or a sharp knife to cut the microgreens just above the soil level. Harvesting can be done selectively, allowing other microgreens to continue growing for subsequent harvests.
- Freshness and Storage: Microgreens are best enjoyed immediately after harvest to maximize their freshness, flavors, and nutritional value. If you need to store them, gently rinse and pat them dry, then place them in an airtight container or zip-top bag lined with a paper towel. Store them in the refrigerator and consume within a few days for the best quality.
- Culinary Uses: Incorporate freshly harvested microgreens into your culinary creations to enhance flavors, add visual appeal, and boost nutritional content. Use them as toppings for salads, sandwiches, wraps, and soups, or as a garnish for various dishes. Their vibrant colors, delicate textures, and concentrated flavors make them a versatile ingredient in both savory and sweet recipes.
VI. Tips for Success
- Start with a Small Vertical Garden: If you’re new to vertical gardening or growing microgreens, start with a small-scale vertical garden to gain experience and build confidence. As you become more familiar with the process, you can expand and customize your vertical garden to suit your preferences and available space.
- Optimize Lighting: Ensure that your vertical garden receives adequate lighting for optimal microgreen growth. If natural light is limited, supplement with artificial grow lights. Position the lights appropriately to provide uniform coverage and adjust the height as the microgreens grow.
- Monitor Moisture Levels: Regularly check the moisture levels in the growing medium of your vertical garden. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot or fungal issues. Maintain consistent moisture by adjusting the watering frequency based on the specific needs of your microgreen varieties and the environmental conditions.
- Rotate the Vertical Garden: To promote even growth and prevent uneven lighting, periodically rotate your vertical garden. This ensures that all sides of the plants receive adequate light exposure and minimizes the risk of plants leaning towards a single light source.
- Experiment with Different Varieties: Explore a wide range of microgreen varieties to diversify your vertical garden and culinary experiences. Try different combinations of flavors, colors, and textures to create unique and enticing displays.
Conclusion
Incorporating microgreens into a vertical garden or green wall brings the joys of gardening to new heights while providing fresh and nutritious greens at your fingertips. By selecting suitable microgreen varieties, setting up the vertical garden properly, and implementing appropriate care and maintenance techniques, you can create a thriving vertical oasis of vibrant, edible greens. The visual impact, culinary versatility, and nutritional benefits of microgreens will enhance your indoor or outdoor space, bringing nature closer to you and transforming your meals into delightful and healthy culinary creations.
Remember to enjoy the process of nurturing your vertical garden and exploring the myriad possibilities that microgreens offer. With a little creativity and dedication, you can create a captivating and sustainable living masterpiece that combines the beauty of vertical gardening with the nutritional powerhouse of microgreens.
References:
- Wong JW, Au CH, Wei C, Wong M. Microgreen: A high-value specialty crop for enhancing human health. J Agric Food Chem. 2016;64(16):pp. 3518-3530. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00879.
- Mir G, Nath AK. Techniques of vertical gardening and its benefits. In: Ramawat KG, Mérillon JM, eds. Sustainable Horticultural Systems: