Thriving Greens in Urban Spaces: Tips for Successful Microgreen Growing in an Apartment or Urban Setting
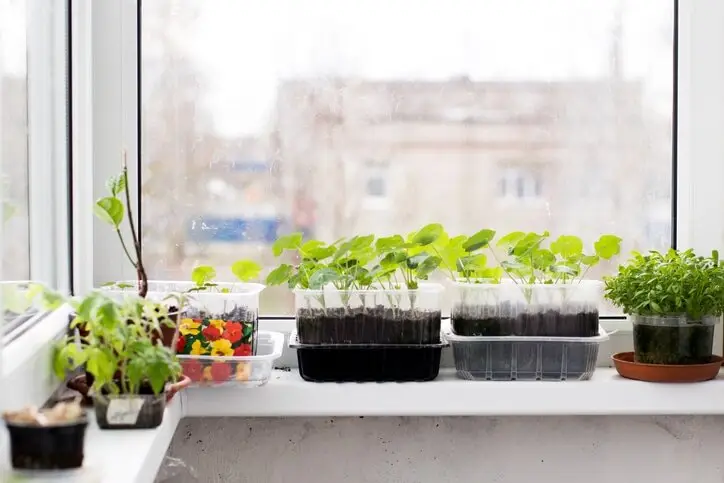

Introduction
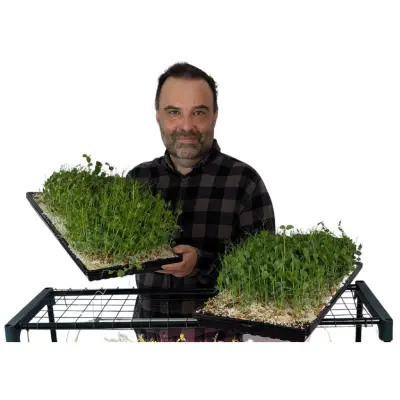
Microgreens have emerged as a popular and rewarding way to grow fresh, nutrient-dense greens in small spaces, making them ideal for apartment dwellers and urban residents. With their vibrant colors, intense flavors, and numerous health benefits, microgreens can be cultivated indoors, allowing urban gardeners to enjoy a bountiful harvest year-round. In this article, we will explore valuable tips and techniques for successfully growing microgreens in an apartment or urban setting, including choosing the right varieties, optimizing space and lighting, and ensuring proper care and maintenance.
I. Selecting Microgreen Varieties for Indoor Cultivation
- Consider Space and Time: Choose microgreen varieties that are suitable for small spaces and have a relatively quick growth cycle. Varieties such as arugula, kale, radish, and broccoli are popular choices as they can be harvested within 1-3 weeks.
- Flavors and Culinary Uses: Select microgreens that complement your culinary preferences and dishes. Experiment with a variety of flavors, including spicy (such as mustard or radish), mild (like lettuce or spinach), and herbaceous (such as basil or cilantro).
II. Optimizing Space and Lighting
- Location Selection: Identify a well-lit area in your apartment that receives natural sunlight for a significant part of the day. South or southwest-facing windows are generally the best options. Alternatively, choose a spot near artificial lighting sources or invest in full-spectrum grow lights for supplemental lighting.
- Vertical Gardening: Maximize your available space by utilizing vertical gardening techniques. Install shelves, hanging planters, or vertical racks to create multiple growing levels for your microgreens. This allows you to grow more plants in a compact area.
- Reflective Surfaces: Utilize reflective materials, such as mirrors or white surfaces, near your growing area to maximize the amount of light reaching the plants. This helps to optimize the available light and ensure even distribution across your microgreens.
III. Choosing the Right Growing Medium and Containers
- Soilless Mixtures: Opt for soilless growing mediums, such as coco coir, peat moss, or vermiculite, which offer excellent moisture retention and drainage. These mediums are lightweight, sterile, and minimize the risk of soil-borne pests or diseases.
- Containers: Select shallow containers or trays with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging and promote proper airflow. Consider using recycled plastic containers or purpose-built microgreen trays that fit well in your available space.
IV. Sowing and Germination Techniques
- Pre-Soaking Seeds: Some microgreen seeds benefit from pre-soaking before sowing. Soak the seeds in clean water for a few hours or overnight to enhance germination rates and speed up the growth process.
- Sowing Density: Pay attention to the recommended sowing density for each microgreen variety. Avoid overcrowding the seeds, as this can lead to poor air circulation and increase the risk of diseases. Follow the guidelines provided with your chosen seeds for optimal spacing.
V. Care and Maintenance
- Watering: Maintain consistent moisture levels in the growing medium by watering carefully. Use a fine mist sprayer or a watering can with a gentle flow to avoid dislodging or damaging the delicate microgreen seedlings. Ensure that excess water drains properly to prevent waterlogging.
- Ventilation and Air Circulation: Good airflow is crucial for preventing mold or fungal growth and promoting sturdy plant growth. Open windows or use a small fan to facilitate air circulation around your microgreens. This helps strengthen the plants and reduces the risk of dampness-related issues.
- Light Exposure: Rotate your microgreens periodically to ensure even light exposure. This prevents the plants from leaning or stretching towards a single light source. Aim for balanced growth by turning the trays or adjusting the position of grow lights every few days.
- Temperature and Humidity: Maintain a suitable temperature range of 60-75°F (15-24°C) for optimal microgreen growth. Avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold drafts. Additionally, monitor the humidity levels in your apartment, as dry indoor environments may require additional humidity through misting or using a humidifier.
VI. Harvesting and Enjoying Microgreens
- Harvesting Time: Microgreens are typically ready for harvest when they have developed their first true leaves. This usually occurs around 1-3 weeks after sowing, depending on the variety. Use clean scissors or a sharp knife to cut the microgreens just above the soil level.
- Freshness and Storage: Microgreens are best enjoyed immediately after harvest to maximize their freshness and nutritional value. If you need to store them, gently rinse and pat them dry, then place them in an airtight container or zip-top bag lined with a paper towel. Store them in the refrigerator and consume within a few days for the best quality.
- Culinary Uses: Incorporate your freshly harvested microgreens into a variety of dishes to add vibrant flavors, textures, and nutrients. Use them as a topping for salads, sandwiches, wraps, soups, or stir-fries. Their delicate and intense flavors make them an excellent addition to both savory and sweet culinary creations.
VII. Troubleshooting and Common Challenges
- Pests and Diseases: Monitor your microgreens for signs of pests, such as aphids or fungal issues like damping off. If detected, address the problem promptly by using organic pest control methods or adjusting watering practices to prevent excess moisture.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Regularly monitor the health of your microgreens and address any signs of nutrient deficiencies. If necessary, incorporate a diluted organic liquid fertilizer to ensure they receive adequate nutrients for robust growth.
- Timing and Succession Planting: Plan your sowing schedule to ensure a continuous supply of fresh microgreens. Stagger the planting of new trays every few days to maintain a steady harvest cycle. This allows you to enjoy a constant supply of microgreens throughout the year.
Conclusion
Growing microgreens in an apartment or urban setting provides a rewarding and sustainable way to cultivate fresh greens and enhance your culinary experiences. By following the tips and techniques outlined in this article, you can successfully nurture thriving microgreen gardens within the limited space and lighting conditions of urban environments. Embrace the joys of indoor gardening, enjoy the vibrant flavors and colors of your homegrown microgreens, and reap the numerous nutritional benefits they offer.
Remember, even in an apartment, you can harness the power of nature and nurture a mini garden that brings freshness and vitality to your urban lifestyle.
References:
- Nitzsche P, Kögel S, Kläring H, et al. Influence of temperature and light intensity on the biomass and carotenoid production of Haematococcus pluvialis grown in outdoor photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol. 2016;28(1):599-609. doi:10.1007/s10811-015-0596-8.
- Manivannan A, Soundararajan P, Muneer S, Ko CH, Jeong BR. Silicon mitigates salinity stress by regulating the physiology, antioxidant enzyme activities, and protein expression in Capsicum annuum ‘Bugwang’. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016:1-13. doi:10.1155