Growing Microgreens at home can relieve the household food budget

Introduction
In an era where the cost of living is constantly rising, families worldwide are seeking innovative ways to maintain a nutritious diet without straining their budgets. One solution that is gaining popularity is the cultivation and consumption of microgreens. These tiny plants pack a powerful nutritional punch and can be easily grown at home, offering a dual benefit of cost savings and enhanced health. This article delves into the world of microgreens, exploring their nutritional benefits, cost-effectiveness, and the simplicity of growing them at home. By the end, you will see how integrating microgreens into your family's diet can be a fun, economical, and nourishing endeavor.
What Are Microgreens?
Microgreens, often hailed as the tiny titans of nutrition, are young vegetable greens that are approximately 1–3 inches tall. They are not to be confused with sprouts or baby greens. While sprouts are just germinated seeds, and baby greens are young leaves of vegetables, microgreens are a stage in between. They are harvested just after the first true leaves have developed, usually within 7 to 14 days after germination.
The world of microgreens is diverse, encompassing a variety of plants. Common varieties include radish, pea, beet, mustard, broccoli, kale, arugula, and cilantro, each with its unique flavor and nutritional profile. This diversity allows for a wide range of tastes and textures to be added to meals, making them a versatile component in the kitchen.
One of the most remarkable features of microgreens is their nutritional density. Studies have shown that these diminutive greens pack a more concentrated amount of nutrients than their mature counterparts. For instance, red cabbage microgreens are noted for their high levels of vitamin C, while cilantro microgreens are rich in carotenoids, a type of antioxidant. This concentration of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants makes microgreens a potent supplement to a regular diet, especially for families seeking to enhance their nutritional intake without increasing their calorie consumption.
The nutritional profile of microgreens can significantly contribute to a family’s health. For example, the high levels of vitamins A, C, and K found in these greens are essential for immune function, skin health, and blood clotting, respectively. Furthermore, the antioxidants present in microgreens can help in reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, Alzheimer's, and certain cancers.
Additionally, the fact that microgreens can be harvested from a variety of vegetables means they can cater to different dietary needs and preferences. Whether a family prefers the peppery taste of radish microgreens or the subtle sweetness of pea shoots, there’s a type of microgreen for every palate.
In conclusion, microgreens are not just a trendy food item; they are a powerhouse of nutrition. Their ability to offer a concentrated burst of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, combined with their diverse range, makes them an ideal addition to any family's diet. As we move forward in exploring the economic and practical benefits of microgreens, it becomes clear that these small greens could play a big role in addressing modern dietary challenges.
Nutritional Benefits of Microgreens
In the quest for a nutritionally rich diet, microgreens emerge as a formidable ally. These tiny greens, harvested just after sprouting, are a powerhouse of essential nutrients and bioactive compounds. The high nutrient density of microgreens makes them not just a culinary delight but a significant contributor to a family’s health and well-being.
Microgreens are particularly renowned for their high concentrations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Studies have shown that these greens contain higher levels of nutrients compared to their mature plant counterparts. For example, microgreen varieties like red cabbage, cilantro, and amaranth are rich in vitamin C, a crucial antioxidant for immune system function and skin health. Similarly, the high levels of vitamin K found in kale and mustard microgreens are essential for bone health and blood clotting.
The benefits of microgreens extend beyond their vitamin content. They are also a rich source of polyphenols, a group of antioxidants linked to a lower risk of heart disease. The antioxidants in microgreens, such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds, play a pivotal role in combating oxidative stress, which is associated with various chronic diseases, including cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
Microgreens like pea shoots and sunflower greens are also an excellent source of dietary fiber, essential for digestive health. Fiber aids in maintaining bowel health, lowers cholesterol levels, and helps control blood sugar levels. This aspect of microgreens is particularly beneficial for families striving to balance a nutritious diet with the challenges of modern lifestyles that often lack sufficient dietary fiber.
Moreover, microgreens can be a vital source of plant-based protein, especially for families adhering to vegetarian or vegan diets. Varieties like pea and sunflower microgreens provide a substantial amount of protein, which is crucial for muscle growth, repair, and overall body function.
The nutritional potency of microgreens also lies in their diverse array of minerals. They contain significant levels of iron, magnesium, and zinc, which are vital for various bodily functions like oxygen transport, enzyme activity, and immune response. For instance, the iron in spinach microgreens is essential for preventing anemia, especially in children and women of reproductive age.
In summary, the inclusion of microgreens in a family's diet offers a multifaceted nutritional boost. These greens provide essential vitamins, antioxidants, fiber, and minerals, all packed into a small, flavorful package. Their ability to deliver concentrated nutrients makes microgreens not just a supplemental food item, but a pivotal component of a wholesome diet, particularly beneficial for families seeking to optimize their health without expanding their calorie intake.
Cost Analysis of Microgreens
In today’s economy, where every penny counts, incorporating microgreens into a family's diet offers not only a nutritional boost but also potential cost savings. When examining the cost-effectiveness of microgreens, it's essential to consider both their upfront costs and long-term savings compared to traditional vegetables.
At first glance, purchasing microgreens from a store can seem more expensive than buying mature vegetables. However, this perspective shifts when considering their nutritional density and yield. Microgreens grown at home can provide a continuous supply of fresh greens at a fraction of the cost of store-bought alternatives. A single tray of microgreens, for instance, can yield enough greens for multiple meals, offering substantial savings over time.
The initial investment in starting a microgreen garden is relatively low. Basic supplies include seeds, a growing medium (like soil or a soilless mix), and a simple container or tray. These materials are generally inexpensive and widely available. Furthermore, microgreens have a quick turnaround time, with many varieties ready to harvest in as little as one to two weeks. This rapid growth cycle means families can have a steady supply of fresh greens without the recurring costs associated with purchasing vegetables from the market.
Another cost-saving aspect of microgreens is their low space requirement. They can be grown in small spaces such as windowsills or balconies, making them accessible to families without access to traditional garden space. This accessibility eliminates the cost of transportation to and from grocery stores or markets, further reducing the overall expense.
Additionally, the longevity of microgreen seeds contributes to cost efficiency. Seeds, when stored properly, can remain viable for years, allowing for repeated plantings from a single purchase. This longevity contrasts with the perishable nature of store-bought vegetables, which can lead to waste and additional expenses.
Moreover, growing microgreens at home can reduce food waste. Since they are harvested and consumed fresh, there's minimal loss of produce, unlike store-bought vegetables that may spoil before they are used. This reduction in waste not only saves money but also aligns with sustainable living practices.
In summary, while the initial cost of microgreens might appear higher than that of traditional vegetables, the long-term economic benefits are substantial. The ability to grow microgreens at home offers ongoing savings, reduces food waste, and provides a continuous supply of nutritious greens. For families working with leaner budgets, microgreens present an efficient, cost-effective solution to enhancing their diet without straining their finances.
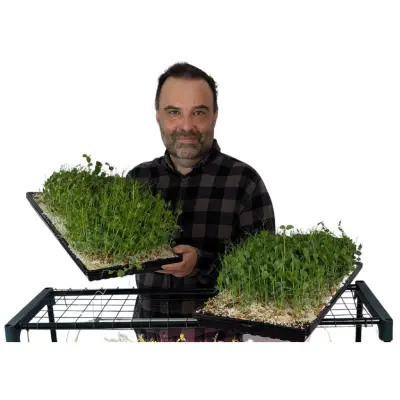
Growing Microgreens at Home
The cultivation of microgreens at home is a surprisingly simple and rewarding process, offering families a sustainable source of fresh, nutrient-rich greens. This practice not only contributes to a healthier diet but also instills a sense of accomplishment and promotes environmental stewardship.
To begin growing microgreens, one needs only a few basic supplies: quality seeds, a growing medium, shallow trays, and a light source. The choice of seeds is vast, with options like radish, kale, arugula, and basil, allowing for a variety of flavors and nutrients. The growing medium can range from soil to soilless mixes like coconut coir or peat moss, which are easily available and affordable.
The process starts with evenly spreading the seeds over the moistened growing medium in a shallow tray. These trays can be placed in areas with natural light, such as a windowsill, or under grow lights if natural light is insufficient. Microgreens require minimal space, making them perfect for urban settings where garden space is limited.
Watering is a critical aspect of microgreen cultivation. The soil should be kept consistently moist but not waterlogged. Using a spray bottle for watering can prevent overwatering and ensure an even distribution of moisture. Proper watering is crucial for the healthy growth of microgreens and prevents issues like mold or uneven germination.
One of the most appealing aspects of growing microgreens is their rapid growth cycle. Most varieties are ready to harvest within 1 to 3 weeks after planting. This quick turnaround allows for a continuous cycle of growth and harvest, providing a steady supply of fresh greens. The simplicity of the harvesting process, which involves snipping the greens just above the soil line, adds to the ease of growing microgreens at home.
Environmental control is another advantage of indoor cultivation. Growing microgreens at home protects them from external factors like pests and harsh weather, reducing the need for pesticides and ensuring a healthier product.
In addition to being an economical choice, homegrown microgreens also offer educational opportunities for children. Engaging in the growing process can teach them about plant biology, responsibility, and the importance of healthy eating habits. This hands-on experience can foster a lifelong appreciation for gardening and nutrition.
In conclusion, growing microgreens at home is a practical, cost-effective, and enjoyable endeavor. It empowers families to take control of a portion of their food supply, reduces dependency on store-bought produce, and contributes to a sustainable lifestyle. With minimal space and effort, families can enjoy the endless benefits of these nutritional powerhouses.
Economic Benefits of Home Cultivation of Microgreens
Growing microgreens at home extends beyond just nutritional advantages; it presents significant economic benefits, especially for families seeking to optimize their budgets in challenging times. The home cultivation of microgreens is not only a gateway to fresh, nutrient-rich produce but also a means to substantial cost savings and financial sustainability.
The most immediate economic benefit of growing microgreens at home is the reduction in grocery bills. Given the relatively high cost of purchasing microgreens from stores or specialty markets, growing them at home can lead to significant savings. The initial investment in seeds, growing medium, and trays is quickly offset by the continuous yield of microgreens. With proper care, a small tray of microgreens can produce a consistent supply of fresh greens, eliminating the need for frequent purchases.
Long-term savings are another major financial advantage. The durability and viability of microgreen seeds mean that a single packet of seeds can last for several seasons, continually providing fresh produce without additional costs. Compared to the recurring expense of buying fresh vegetables, which can fluctuate in price due to seasonal changes and market conditions, home-grown microgreens offer a stable and predictable alternative.
Additionally, the quick growth cycle of microgreens enhances their economic value. With harvest times as short as one to two weeks, families can experience a rapid return on their initial investment. This quick turnaround not only ensures a regular supply of fresh greens but also allows for better budgeting and financial planning.
The versatility of microgreens also contributes to their economic benefits. They can be grown year-round, irrespective of the external climate, using indoor spaces like kitchen counters or windowsills. This continuous production capacity eliminates the seasonal constraints often associated with traditional vegetable gardening, providing families with a reliable source of fresh produce throughout the year.
Furthermore, the home cultivation of microgreens can reduce food waste, a hidden cost in many households. Unlike store-bought produce that may spoil before it's consumed, microgreens are harvested fresh and used immediately, ensuring no wastage and maximizing the value of every harvest.
Engaging in the home cultivation of microgreens also provides intangible economic benefits. It fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of food sources, encouraging sustainable living practices. Moreover, the skills and knowledge gained from growing microgreens can be applied to other gardening endeavors, potentially leading to further cost savings and self-sufficiency.
In conclusion, the economic benefits of growing microgreens at home are manifold. They offer an affordable, sustainable, and rewarding way to enhance a family's diet, providing both immediate and long-term financial advantages. In times of economic uncertainty, the cultivation of microgreens represents a smart, proactive approach to household budgeting and nutrition.
Incorporating Microgreens into Meals
Microgreens, with their vibrant colors, diverse textures, and rich flavors, not only elevate the nutritional content of meals but also enhance their gastronomic appeal. Integrating these tiny greens into a family's diet can be both a culinary adventure and a step towards healthier eating habits.
One of the easiest ways to incorporate microgreens into daily meals is by using them as garnishes. Their fresh, often intense flavors add a new dimension to dishes. For instance, radish microgreens, with their peppery taste, can be sprinkled over soups and stews for an added zing. Similarly, cilantro or basil microgreens can be used to top tacos, pizzas, or pasta, infusing these familiar dishes with new flavors and nutrients.
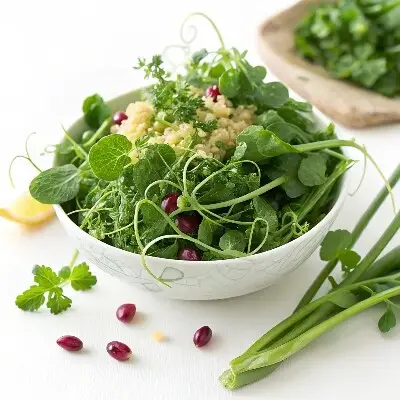
Salads are another perfect vehicle for microgreens. Mixing different types of microgreens, such as arugula, kale, and beet greens, can create a salad that is not only visually appealing but also packed with diverse nutrients. Adding microgreens to salads not only boosts their vitamin and mineral content but also introduces a variety of textures and flavors, making the salads more interesting and satisfying.
Microgreens can also be seamlessly incorporated into smoothies and juices. For families with children, this can be an excellent way to introduce them to the health benefits of microgreens. Blending green microgreens like spinach or kale with fruits can mask their taste while still providing their nutritional benefits, making it a kid-friendly option.
For a heartier option, microgreens can be incorporated into omelets, sandwiches, and wraps. The addition of microgreens to these dishes not only increases their nutritional value but also adds a fresh crunch and burst of flavor. This versatility makes microgreens a convenient addition to any meal, without requiring significant changes to existing dietary habits.
Moreover, involving children in the process of growing and then using microgreens in cooking can be an educational and fun experience. It can teach them about where food comes from and the importance of eating fresh, nutrient-rich foods. Cooking with microgreens can become a family activity, encouraging healthier eating habits and fostering a connection with the food they consume.
In conclusion, incorporating microgreens into meals is an easy, delicious, and versatile way to enhance the nutritional value of a family's diet. From simple garnishes to being integral components of main dishes, microgreens offer a spectrum of possibilities for creative and health-conscious cooking. Their inclusion in daily meals represents a simple yet effective step towards a more nutritious and enjoyable dietary lifestyle.
Environmental Benefits of Growing Microgreens
The cultivation of microgreens at home extends beyond personal health and financial savings; it also has a positive impact on the environment. In an age where sustainable living is becoming increasingly important, growing microgreens represents a small but significant step towards a more eco-friendly lifestyle.
One of the primary environmental benefits of growing microgreens is the reduction in food miles. Food miles refer to the distance food travels from where it is grown to where it is consumed. By growing microgreens at home, families can drastically reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting produce from farms to supermarkets and then to homes. This reduction in transportation not only lowers carbon emissions but also decreases the overall consumption of fossil fuels.
Home cultivation of microgreens also contributes to reducing packaging waste. Commercially sold greens often come in plastic containers or bags, contributing to plastic waste. When families grow microgreens at home, they eliminate the need for this packaging, thereby reducing their plastic footprint and helping to mitigate the global plastic pollution crisis.
Another significant environmental advantage of growing microgreens is the efficient use of water. Microgreens require relatively little water compared to traditional gardening, which is particularly important in areas facing water scarcity or drought conditions. This efficient use of water resources makes microgreen cultivation a sustainable practice, aligning with the principles of responsible water management.
Additionally, growing microgreens at home can improve biodiversity. By cultivating a variety of microgreens, families can contribute to the preservation of different plant species, many of which are not typically found in regular grocery stores. This diversity is not only beneficial for personal health but also supports a healthier ecosystem.
Moreover, the practice of growing microgreens encourages the use of organic and non-toxic methods. As microgreens are typically grown in controlled indoor environments, the need for pesticides and herbicides is greatly reduced, if not eliminated. This approach promotes a cleaner and safer environment by preventing the introduction of harmful chemicals into the soil and water systems.
The process of growing microgreens also promotes environmental education and awareness. Families engaged in this practice gain a deeper understanding of sustainable agriculture and the importance of eco-friendly practices. This knowledge can inspire further actions towards sustainability, creating a ripple effect that extends beyond the household.
In conclusion, the home cultivation of microgreens offers considerable environmental benefits. By reducing food miles, packaging waste, water usage, and chemical inputs, and by promoting biodiversity and environmental education, growing microgreens at home is a powerful tool in the pursuit of a sustainable and eco-conscious lifestyle.
Challenges and Solutions in Growing Microgreens
While the cultivation of microgreens offers numerous benefits, aspiring growers may encounter certain challenges. However, with the right knowledge and approach, these obstacles can be effectively overcome, ensuring a successful and rewarding growing experience.
One common challenge in growing microgreens is inadequate or excessive moisture, leading to issues like mold growth or poor seed germination. To combat this, it's essential to maintain a balance in watering. Using a spray bottle to mist the seeds and soil can provide even moisture without over-saturating the medium. Additionally, ensuring proper ventilation around the growing area can prevent the buildup of excess humidity, thereby reducing the risk of mold.
Another hurdle can be insufficient light, which may result in leggy and weak microgreens. This issue can be resolved by providing a consistent light source, such as placing the growing trays near a sunny window or using artificial grow lights. It's important to ensure that the microgreens receive adequate light for at least 4-6 hours a day to foster robust growth.
Pest infestations, though less common in indoor settings, can still occur. To tackle this, growers can use natural pest control methods such as neem oil or introduce beneficial insects. Keeping the growing area clean and monitoring the plants regularly can also help in early detection and management of pests.
Nutrient deficiencies might also pose a challenge, especially when using a soilless growing medium. In such cases, applying a mild, organic liquid fertilizer can provide the necessary nutrients for the microgreens to thrive. However, it's crucial to avoid over-fertilization, which can harm the delicate plants.
For beginners, selecting the right seeds and growing medium can be daunting. Researching and starting with easy-to-grow varieties like radish, peas, or sunflower can build confidence. Using a quality growing medium that suits the chosen seeds is equally important for successful germination and growth.
Moreover, timing the harvest can be tricky. Harvesting too early may yield underdeveloped greens, while waiting too long can lead to tough, overgrown plants. Observing the growth and harvesting when the first true leaves appear is usually the best practice.
Finally, space constraints might be a concern for some. However, microgreens require minimal space and can be grown in small containers or trays, making them ideal for compact urban dwellings. Utilizing vertical space with shelving can also maximize the growing area.
In conclusion, while growing microgreens at home can present challenges, these can be effectively addressed with the right techniques and a bit of experimentation. By overcoming these hurdles, families can enjoy the full spectrum of benefits that these nutritious greens offer.
Embracing the Microgreen Movement: A Conclusion
As we reach the conclusion of our exploration into the world of microgreens, it's clear that these tiny greens are more than just a culinary trend. They represent a confluence of nutritional, economic, and environmental benefits that align remarkably well with the needs of modern families. The journey of understanding microgreens – from their nutrient-packed profiles to the ease and sustainability of growing them at home – opens up new avenues for enhancing our diets and lifestyles.
Microgreens stand out as nutritional powerhouses, offering a dense concentration of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Their incorporation into daily meals can significantly elevate the nutritional quality of a family's diet, contributing to better overall health. This aspect is particularly vital in the context of rising health concerns and a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare through diet.
Economically, the home cultivation of microgreens presents a compelling case. With the increasing cost of groceries and the financial strain on many households, growing microgreens offers a practical solution to reduce food expenses. The low start-up costs, minimal space requirements, and the quick and abundant yield of microgreens make them an ideal choice for families looking to optimize their budgets. This economic advantage, coupled with the joy and satisfaction of growing one's own food, adds a unique value to the practice.
Environmentally, the microgreen movement aligns with the growing global consciousness towards sustainable living. By reducing food miles, minimizing packaging waste, and using eco-friendly growing practices, microgreen cultivation contributes to a healthier planet. This practice not only lessens the environmental footprint of our food choices but also serves as an educational tool for younger generations, fostering a deeper understanding of and respect for our ecological systems.
Furthermore, the challenges associated with growing microgreens, though present, are easily surmountable. With a bit of practice and patience, even novice gardeners can successfully cultivate these greens. The process of overcoming these challenges not only enhances gardening skills but also instills a sense of achievement and resilience.
In summary, the cultivation and consumption of microgreens offer a multi-faceted solution to contemporary issues related to nutrition, economy, and the environment. This simple yet impactful practice has the potential to revolutionize our approach to food and wellness. By embracing the microgreen movement, families can take a significant step towards a healthier, more sustainable, and economically savvy lifestyle. The journey of growing and incorporating microgreens into our diets is an enriching experience, full of learning, growth, and, most importantly, a step towards a better future.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The author and publisher of this article are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of any suggestions, preparations, or procedures described in this article.